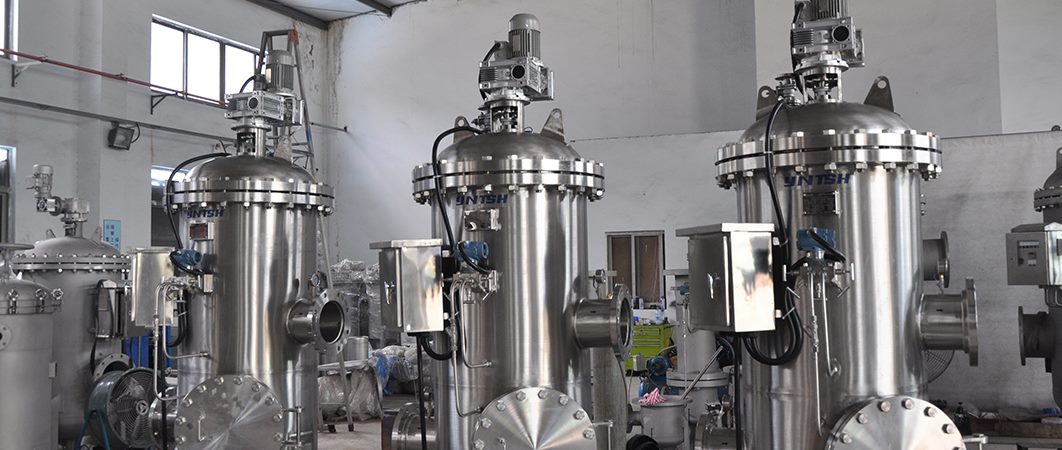
What Is an Industrial Filter Housing and How Does It Work?
Industrial filtration systems rely on more than just filter elements. At the core of every reliable filtration system is the industrial filter housing, which provides structural support, pressure containment, and controlled flow paths. Understanding what a filter housing is and how it works is essential for engineers, system designers, and operators involved in water treatment, chemical processing, and other industrial applications.
What Is an Industrial Filter Housing?
An industrial filter housing is a pressure-rated vessel designed to hold one or more filter elements and direct process fluid through those elements to remove solid contaminants.
It serves as the mechanical framework that enables effective, safe, and repeatable filtration under defined operating conditions.
Unlike filter elements, which perform the actual separation, the filter housing ensures:
• Controlled flow direction
• Pressure containment
• Proper sealing and element positioning
• Safe operation within system limits
Industrial filter housings are widely used in water treatment, chemical processing, refining, food and beverage production, power generation, and seawater systems.

Filter Housing vs. Filter Element
Although closely related, filter housings and filter elements serve different roles.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Filter Housing | Holds filter elements, manages flow and pressure, ensures system integrity |
| Filter Element | Performs particle removal or separation |
A high-quality filter element cannot perform effectively without a properly designed housing. Mismatched housings often lead to bypass leakage, excessive pressure drop, or premature element failure.
Main Components of an Industrial Filter Housing
A typical industrial filter housing consists of several key components:
• Housing shell: The pressure-containing body, usually made from stainless steel, duplex steel, or coated carbon steel
• Inlet and outlet connections: Direct fluid flow into and out of the housing
• Element support structure: Ensures correct positioning and prevents deformation under pressure
• Sealing system: Gaskets or O-rings that prevent internal bypass
• Cover or closure system: Allows safe access for maintenance and element replacement
Each component must be engineered to match the operating pressure, temperature, and chemical characteristics of the process fluid.
How Does an Industrial Filter Housing Work?
The operating principle of an industrial filter housing is straightforward and highly reliable.
• Process fluid enters the housing through the inlet connection
• Flow is distributed evenly across the filter element surface
• Solid contaminants are retained on or within the filter element
• Clean fluid exits through the outlet connection
• As solids accumulate, differential pressure gradually increases
When the pressure drop reaches a predefined limit, the filter element is cleaned or replaced, depending on the housing and element type.
This controlled process protects downstream equipment and ensures consistent filtration performance.

Types of Industrial Filter Housings
Industrial filter housings are classified based on structure and operating method.
Designed for high filtration accuracy
Commonly used for RO pretreatment, product polishing, and membrane protection
Suitable for high flow rates and moderate filtration accuracy
Simple operation and cost-effective maintenance
• Self-Cleaning Filter Housings
Automatically remove accumulated solids
Ideal for seawater intake, cooling water, and high-solids applications
• Inline and Duplex Housings
Inline housings support continuous operation with shutdown during maintenance
Duplex housings allow element change without stopping system flow
Typical Industrial Applications
Industrial filter housings are used across a wide range of industries:
• Water treatment: Pretreatment, membrane protection, and tertiary filtration
• Chemical processing: Catalyst protection, slurry filtration, solvent purification
• Seawater systems: Intake filtration and desalination pretreatment
• Food and beverage: Sanitary-grade filtration for product quality assurance
• Power generation: Cooling water and auxiliary system protection
Each application places different demands on housing material, pressure rating, and internal design.
Why Proper Filter Housing Design Matters
A properly selected and engineered filter housing ensures:
• Stable system operation
• Reduced maintenance frequency
• Longer filter element life
• Lower operating costs
• Improved safety and compliance
Conversely, improper housing selection is a common cause of leakage, corrosion failure, and unplanned downtime.
An industrial filter housing is a critical component that enables effective filtration by providing structural support, pressure containment, and controlled flow. Understanding how filter housings work, and how they differ from filter elements is essential for designing reliable industrial filtration systems.